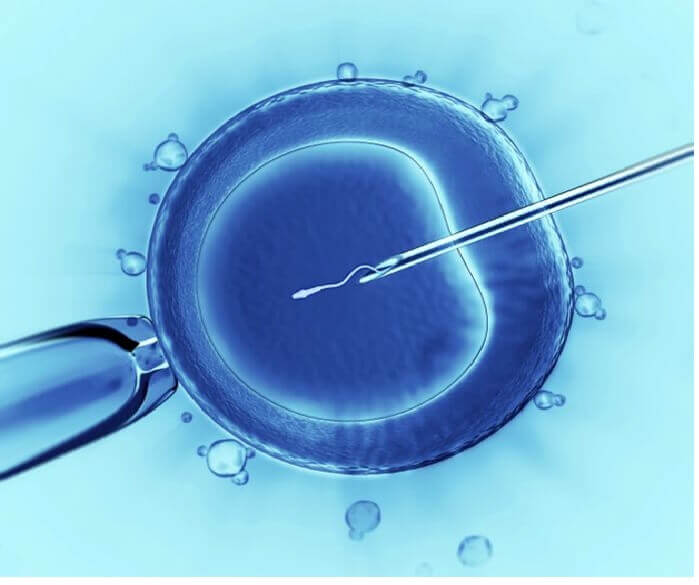

ICSI, short for intracytoplasmic sperm injection, is a specialized technique used in cases of severe male factor infertility and obstructive azoospermia. The process of ICSI follows the same steps as in IVF, with the main difference lying in the method of fertilization. In ICSI, each individual oocyte (egg) is carefully injected with a single healthy sperm using precise micromanipulation devices under a microscope. The steps involved in ICSI are as follows:
The administration of injections to the female partner begins either on day 21 or day 2 of her menstrual cycle. The growth of follicles, which contain the developing eggs, is closely monitored through a series of scans. This allows the physician to adjust the dosage of the injections as needed. Once the follicles have reached maturity, egg retrieval is planned after administering an HCG trigger. The HCG trigger helps the eggs complete their final maturation steps and prepares them for eventual ovulation.
The process of egg retrieval is performed under general anesthesia. Using a transvaginal ultrasound guided needle, all the follicles containing the eggs are carefully aspirated. These retrieved follicles are then examined under a microscope to identify and confirm the presence of the eggs. This meticulous examination ensures accurate assessment and handling of the eggs for further steps in the IVF process.
In the next stage of the IVF process, a meticulous procedure called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is performed, where each individual egg is delicately injected with a single sperm. This precise technique ensures the direct fertilization of each egg. Following this, the resulting embryos are carefully incubated for a period of three to five days. During this incubation period, the embryos undergo development and reach the optimal stage for potential transfer or further laboratory procedures.
Using a specialized catheter, the embryo transfer procedure is performed on either day 3 or day 5 after fertilization. This crucial step involves delicately transferring the developed embryos into the woman’s uterus. The selection of the transfer day is based on various factors and the guidance of the medical team. The special catheter ensures precise placement of the embryos into the uterine cavity, maximizing the chances of successful implantation and the beginning of a healthy pregnancy journey.
It is recommended to undergo a pregnancy test approximately two weeks after the embryo transfer procedure. This waiting period allows sufficient time for the pregnancy hormone levels to rise to a detectable level. It is important to follow the recommended timeline to ensure accurate and reliable results. The pregnancy test serves as a significant milestone in determining the success of the embryo transfer and provides valuable information about the next steps in the fertility journey.
On the day of egg retrieval, a semen sample is required. It is advisable for the male partner to abstain from ejaculation for a period of 2 to 6 days prior to providing the sample. Ideally, the sample should be produced at the fertility center. However, if necessary, it can be brought from home as long as it is delivered to the center within 45 minutes of production. In cases where there are difficulties with sperm production or male infertility, sperm retrieval procedures such as Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESA) may be performed to obtain sperm directly from the testes. These procedures are conducted under medical supervision to ensure the best possible chances of successful fertilization during the IVF process.