Discover the benefits of advanced laparoscopy surgery for precise and effective treatment

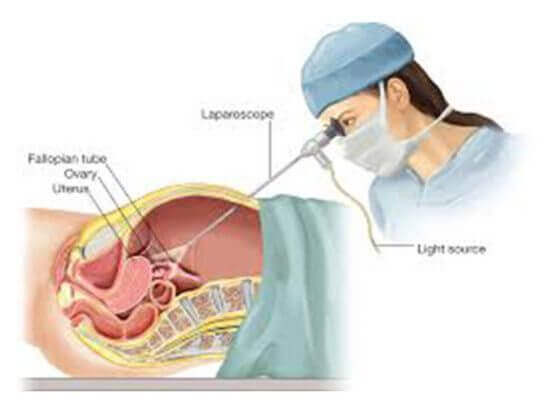
Certainly! Laparoscopy, also known as keyhole surgery or minimally invasive surgery, is a surgical procedure that allows doctors to examine and operate on the internal organs using small incisions. It involves the use of a laparoscope, a long, thin tube with a light and camera attached to it.
During a laparoscopy, several small incisions are made in the abdomen, typically measuring about 0.5 to 1 centimeter in length. Carbon dioxide gas is then introduced into the abdominal cavity to create space and improve visibility. The laparoscope is inserted through one of the incisions, allowing the surgeon to visualize the organs on a monitor.
Additional instruments may be inserted through the other incisions to perform various procedures, such as removing diseased tissues, taking biopsies, or repairing organs. These instruments are usually long and thin, designed to fit through the small incisions.